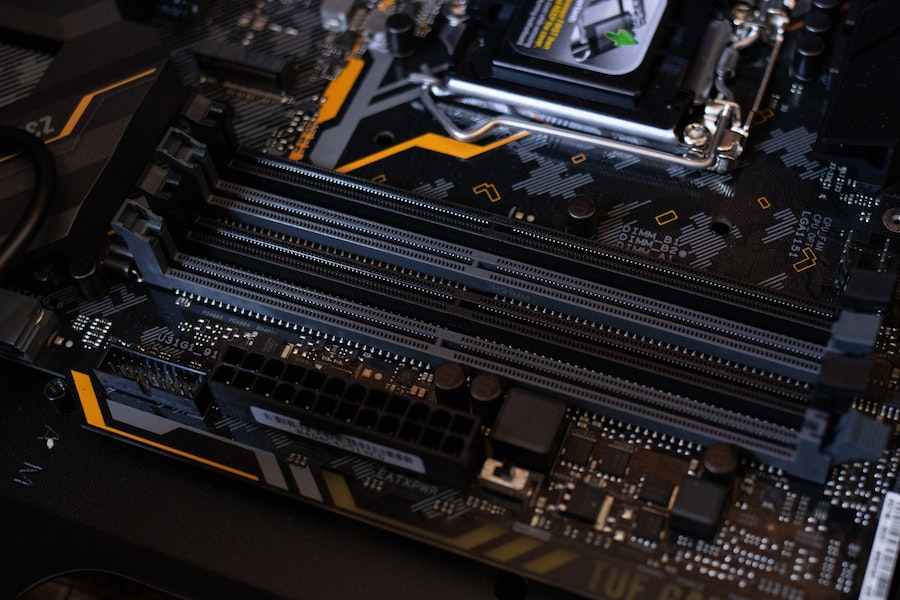
NVMe is a great way to upgrade the performance of your computer, but before you go ahead and make the upgrade, you need to make sure your motherboard supports NVMe. Understanding the basics of NVMe and motherboards can help you determine if your motherboard has the necessary components to support the technology. NVMe is an advanced storage technology that utilizes the PCIe interface to provide fast data transfer speeds. It works by allowing for direct communication between the processor and the storage device, allowing for faster data read and write speeds. Your motherboard must have an M.2 slot with an NVMe-compatible connector to support the technology. Additionally, your motherboard must have a compatible chipset and BIOS to ensure compatibility. With the right components and understanding, you can determine if your motherboard is capable of supporting NVMe.
Does My Motherboard Support NVMe?
The short answer is it depends. When it comes to determining whether or not your motherboard supports NVMe, the first thing you need to do is check what type of motherboard you have. Different motherboards support different types of memory, so it’s important to know what type of motherboard you have in order to know if it supports NVMe.
How To Motherboard Support NVMe?
Check your Bios settings
The first thing you should do when you’re building a computer to make sure your motherboard is able to support NVMe is to check your Bios settings. When you first boot up your computer, you’ll see a menu called the “BIOS” menu. The BIOS menu will display your computer’s basic settings, so you can make any necessary adjustments before you actually start using your computer. One of the settings you’ll want to make sure is configured correctly is NVMe. Different motherboard manufacturers use different terminology for their NVMe settings, but it’s easy to find out what yours is. Just Google your motherboard model and “BIOS settings,” and you’ll likely find a list of the correct settings for your board. Once you’ve found your motherboard’s NVMe settings, make sure they’re configured correctly. Most motherboards can use NVMe, but some will require you to enable it manually in the Bios settings. Make sure your motherboard’s NVMe settings are configured correctly, and you’ll be able to safely use any NVMe drive in your motherboard.
Check the form factor of your NVMe drive
While the motherboard form factor is a critical factor in determining whether or not your motherboard can use an NVMe drive, it’s also essential to check the form factor of the drive itself. Not all NVMe drives use a 2.5” form factor, and not all motherboards can support M.2 drives. Some motherboards can use both 2.5” and M.2 drives, but if yours is one of them, make sure you use the correct form factor. 2.5” drives fit in a 3.5” drive bay, but they’re not designed to be used in a standard desktop computer. They’re designed for use in high-end workstations, so you’re better off using an M.2 drive on your desktop computer.
Ensure your motherboard has the right connection type
Before you buy an NVMe drive, you should ensure your motherboard has the right connection type to support it. The two most common connection types for NVMe drives are SATA and PCIe. It’s crucial that you get the right type of connection for your motherboard, otherwise, it won’t be able to use the drive. If your motherboard uses a SATA connection type, you won’t be able to use an NVMe drive with a PCIe connection. You can check your motherboard’s connection type in the Motherboard Manual. You can find the motherboard manual on the manufacturer’s website, and it’s likely to have a tab or link on their homepage that links directly to the motherboard manual. Once you’ve found the motherboard manual, all you need to do is look for the connection type listed under “storage.” You can also check the form factor of your drive, and it will tell you if it’s SATA or PCIe.
Look for M.2 expansion slots
Once you’ve ensured your motherboard can handle an NVMe drive, and you’ve found the right driver for your system, you should also look for M.2 expansion slots on your motherboard. If your motherboard doesn’t support SATA or PCIe, you can use M.2 expansion slots to add an M.2 card that will work with NVMe drives. If you already own a motherboard that can’t handle NVMe drives, you can buy an M.2 expansion card. Motherboards with M.2 expansion slots are typically more expensive than standard motherboards, but they’re worth it if you need to add an M.2 card to support NVMe.
Upgrade your BIOS
Finally, if you’ve tried all these tips and your motherboard still doesn’t support NVMe, you can try upgrading your BIOS. Every motherboard manufacturer releases BIOS updates, and they often fix bugs and add new features. If your motherboard can’t use NVMe, there may be an update that adds support for it, so make sure you check for BIOS updates. You can usually find the BIOS update on the manufacturer’s website, or you can use the “BIOS update” option in your computer’s BIOS menu. When you’re updating your BIOS, make sure you do it correctly. It’s a relatively simple process, but it’s easy to mess up if you don’t follow the instructions carefully.
What Components Are Needed To Support NVMe?
- To support NVMe, your computer’s motherboard must have an M.2 slot with an NVMe-compatible connector
- Additionally, your motherboard must have a compatible chipset and BIOS to ensure compatibility.
- This includes a PCIe M.2 slot and an NVMe-compatible BIOS/chipset.
How To Determine If Your Motherboard Supports NVMe
- There are several ways you can determine if your motherboard supports NVMe.
- First, you can check the motherboard’s technical specifications.
- You can also check the motherboard’s manual and look for an M.2 slot with an NVMe connector.
- You may also see a sticker on the motherboard that indicates whether or not it supports NVMe.
Exploring The Different NVMe-Compatible Chipsets
- There are many different chipsets available that support NVMe. These include Intel’s X99 and X299, as well as their newer Z370, Z390, and Z490; AMI’s 988X; and NVIDIA’s M.2 PCIe NVMe.
- These chipsets can differ in terms of the number of lanes and the speed of data transfer. When selecting a motherboard, you should always ensure it uses a chipset that supports NVMe.
- You can determine if a chipset supports NVMe by checking if it has at least two PCIe 3.0 lanes. This means there are at least two lanes that can be used for the NVMe device.
- Some chipsets, such as the Z390, are specifically designed to support the more advanced NVMe devices.
Benefits Of NVMe
- There are many benefits to upgrading to an NVMe SSD. First, the technology is capable of providing significantly faster data transfer speeds. This is because NVMe uses a technique called parallelism, which allows multiple devices to simultaneously send and receive data.
- This means that the data is processed much faster than with traditional storage devices.
- NVMe is also more power efficient than other storage devices, which means it can help reduce your energy cost.
- This is because the devices can run at lower voltages without compromising performance.
- NVMe also offers greater reliability and durability than traditional storage devices. This is due to the fact that the devices are solid-state, which makes them less susceptible to damage.
- While NVMe can provide a number of benefits, there are also some drawbacks to be aware of. First, the technology is more costly than other storage devices. It is also not compatible with older motherboards.
Tips For Upgrading Your Motherboard For NVMe Support
- You should check and see if your motherboard has a slot for NVMe. This can be found in the manual or on the manufacturer’s website. If your motherboard does not have a slot for NVMe, you cannot use an NVMe storage device.
- You should also check to see if you have the latest BIOS version installed on your computer. This is because not all motherboards are compatible with all devices, and updating the BIOS may fix any incompatibility issues you are having. You can also visit the manufacturer’s website to see if there is a newer version of BIOS available.
- If you want to use an NVMe storage device with Windows 7, 8, or 8.1, then you will need to install drivers from the manufacturer of your device before proceeding with the installation of Windows 10 (which already comes with drivers).
- Check the number of lanes available on your motherboard. This can be found in the manual or on the manufacturer’s website. If there are not enough lanes, you will need to purchase a new motherboard that supports NVMe.
- If you are using a laptop, check its PSU wattage rating and make sure it is enough to support the device. Otherwise, you may experience issues with instability while running demanding software or games. The same applies if you are using a desktop computer, but in this case, check how many watts of power your PSU can provide and make sure it is enough to support the device. You should also check how many watts of power are needed by your PSU for stability when using an NVMe storage device with demanding programs and games. If it does not have enough watts of power for stability, then you
Summary
NVMe is a great way to upgrade the performance of your computer, but before you go ahead and make the upgrade, you need to make sure your motherboard supports NVMe. Understanding the basics of NVMe and motherboards can help you determine if your computer is compatible with the technology. NVMe is an advanced storage technology that utilizes the PCIe interface to provide fast data transfer speeds. It works by allowing for direct communication between the processor and the storage device, allowing for faster data read and write speeds.